[最も欲しかった] yield point vs proportional limit 652031-What is the difference between proportional limit and yield point
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe proportional limit and the yield point are close to one another on a stressstrain curve, but they each have a different representation and thus do not corresponds to the same point on the curve The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress level on the engineering stressstrain curve, ie the maximum stress that can be withstand by a structure in tensionUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher
Tensile Testing
What is the difference between proportional limit and yield point
What is the difference between proportional limit and yield point-Yield point is essentially the same, except that it is usually defined when the permanent strain reaches a particular level such as 02% Neither the elastic limit nor the yield point can be identified from a graph in which the load is continuously increased In order to identify these points the load must be removedBut their values are fairly close to each other in many cases



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora
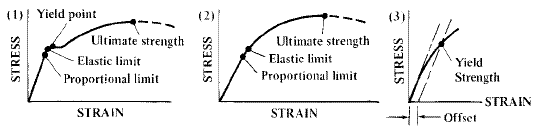
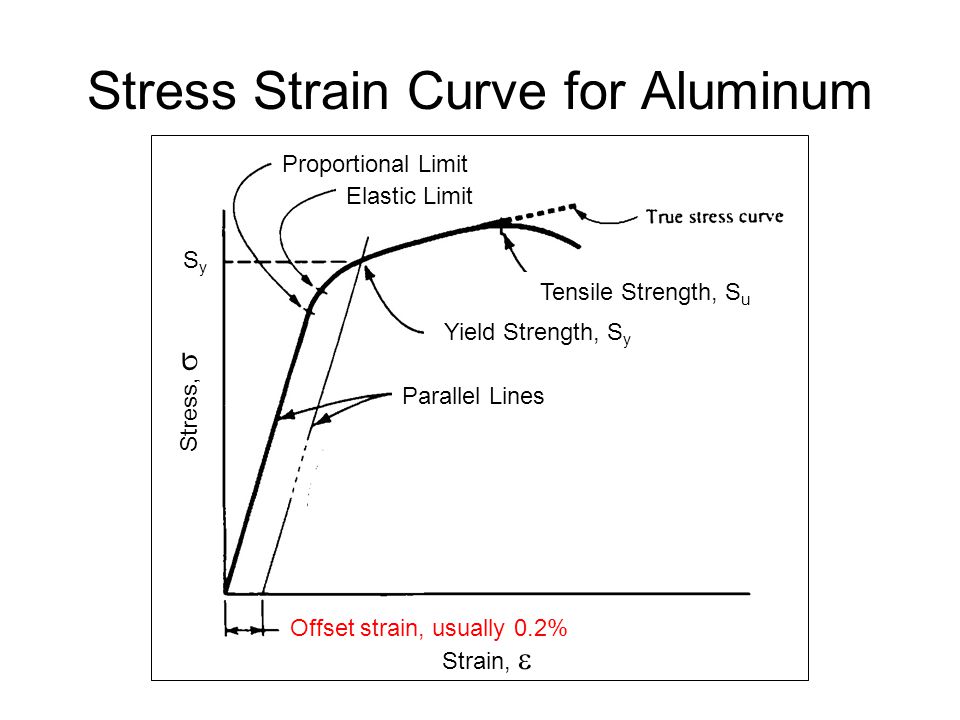
In the figure, the yield strength is represented by the point of intersection of the parallel line to the stressstrain curve The proportional limit, elastic limit, and yield strength are defined differently;The proportional limit is the point on a stressstrain curve where the linear, elastic deformation region transitions into a nonlinear, plastic deformation region In other words, the proportional limit determines the greatest stress that is directly proportional to strainYield point is well defined and shown on graph for mild steel and it's beyond elastic limit For other materials like copper or aluminum is defined as the point of intersection of stressstrain curve and a line drawn parallel to linear part fron 02 percent deformation (strain ε) and it is also beyond the elastic limit
O Fracture Strength O Proportional Limit O Yield Strength O Ultimate Strength Stress Strain The Property Of A Material To Resist Deformation Under Unit Stress Is Known As Ere To Search Bi 99Elastic Limit Is the point on the stress/strain curve where the material will behave elastically ie will return to its original shape without leaving any permanent deformations Yield Point The yield point is the point on a stress–strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviourHow is Proportional Limit Different from Yield Strength?
Tensile tests are used to determine the modulus of elasticity, elastic limit, elongation, proportional limit, reduction in area, tensile strength, yield point, yield strength and other tensile properties The main product of a tensile test is a load versus elongation curve which is then converted into a stress versus strain curveSimilar to the elastic limit, the yield strength of a material can also occur beyond the material's proportional limit Unlike the elastic limit, the yield strength on a stressstrain curve has been defined by ASTM and ISO test standards Depending on the material's stressstrain behavior at yield, a preferred yield calculation is specified by the chosen standardBrittle materials do not exhibit any yield point So they do not have yield strength Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) is considered as the failure criteria for brittle material In ductile materials, yield strength is much lower than ultimate strength For ductile materials, ultimate strength is roughly 15 times higher than yield strength



Stress Strain Curve Diagram Relationship And Explanation Mechanical Education


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora
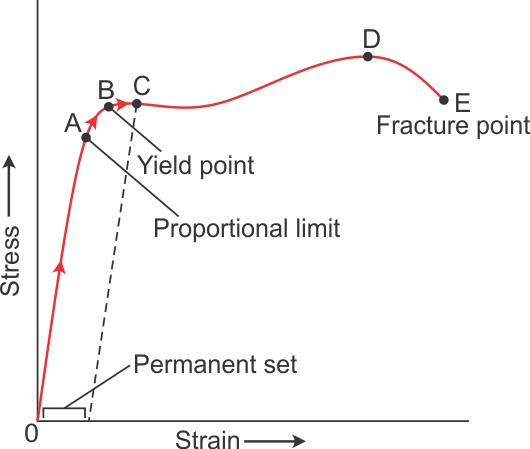
Between the proportional limit and the yield point the Hooke's Law becomes questionable between and strain increases more rapidly References Materials Science US Department of Energy, Material Science DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 1 and 2 January 1993These regions and points are Proportional limit;A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau


Tensile Testing
How is Proportional Limit Different from Yield Strength?As stress at proportional limit There is no clearly defined ultimate stress for this property Shear strength parallel to grain—Ability to resist internal slipping of one part upon another along the grain Values presented are average strength in radial and tangential shear planes Impact bending—In the impact bending test, a hammerUp to the limit of proportionality, stress directly followed the strain This means ratio of stress and strain remains constant Elastic limit Up to this limit (point B), is material will regain its original shape is unloaded Point B is known as elastic point Yield limit When material is loaded beyond its elastic limit, it will not regain its original shape



Solve This Q Explain Stress Strain Curve With Diagram Physics Mechanical Properties Of Solids 1229 Meritnation Com


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
In most metallic materials the elastic limit and proportional limit are essentially the same Offset Yield Point (proof stress) Due to the lack of a clear border between the elastic and plastic regions in many materials, the yield point is often defined as the stress at some arbitrary plastic strain (typically 02%)Fracture or breaking point;Dorothy Distefano Date February 03, 21 Scientist with beakers Yield point, also known as yield strength or elastic limit, is an important value to consider when selecting a material for design and building applications, particularly when there are significant loads or stresses being applied



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets


2 3 2 A Sim Tensiletesting 1 Docx
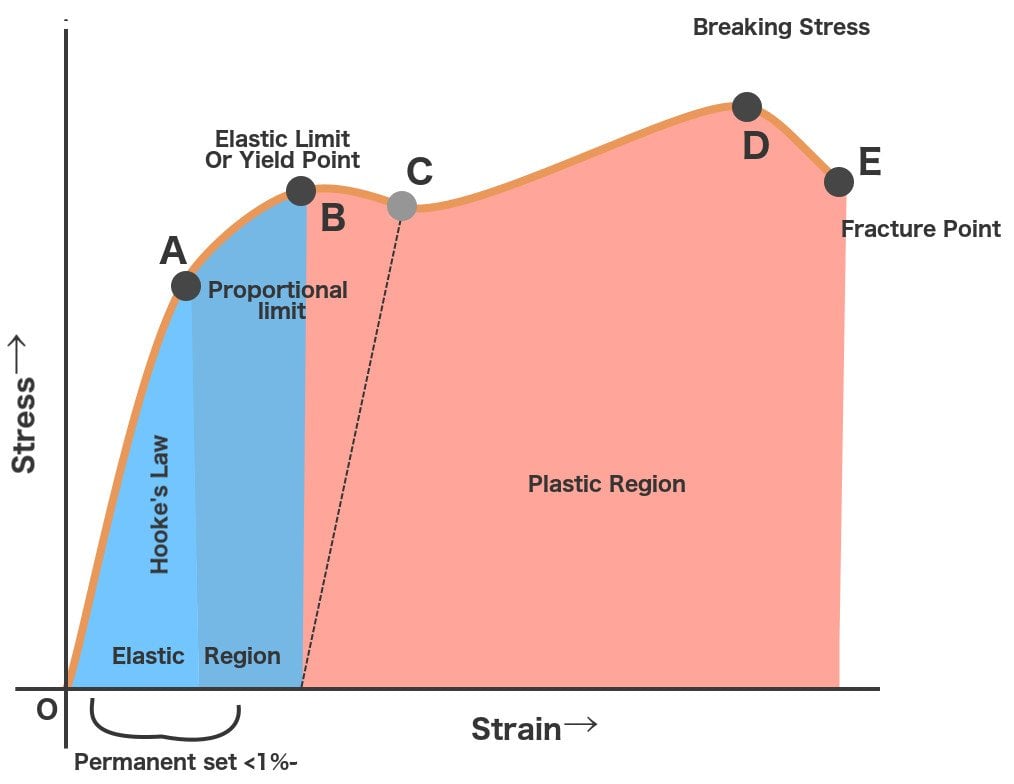
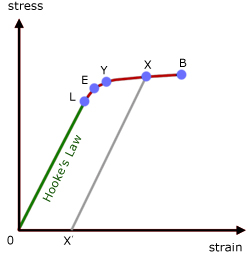
A study of stressstrain diagrams shows that the yield point is so near the proportional limit that for most purposes the two may be taken as one However, it is much easier to locate the former For materials which do not possess a welldefined yield point, one is actually "invented" by the use of the socall offset methodProportional limit is the maximum stress for which strain remains proportional to stress As it is usually not obvious, industry accept to use offset method in/in Yield stress is stressThe point OA in the graph is called the proportional limit (ii) Elastic Limit It is the point in the graph up to which the material returns to its original position when the load acting on it is completely removed Beyond this limit, the material doesn't return to its original position and a plastic deformation starts to appear in it (iii) Yield Point


Http Www Avant Garde Engineering Statics Statics8 Pdf


What Is The Difference Between Yield Point And Elastic Limit Quora
A = proportional limit D = elastic limit – Beyond this point, the material is no longer elastic B= Yield point (in fig a) – A stress level beyond which the material would demonstrate high strain for a small stress (perform like a plastic) B= Yield strength (point B in fig b) – Stress that will induce permanent set (anO Fracture Strength O Proportional Limit O Yield Strength O Ultimate Strength Stress Strain The Property Of A Material To Resist Deformation Under Unit Stress Is Known As Ere To Search Bi 99Where the material follows the Hook's law The upper yield point in the curve is the peak value reached after the linear part;



Tensile Strength And Elongation At Yield Astm D638



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
Proportional limit and yield point 11 enero, 21 0Similar to the elastic limit, the yield strength of a material can also occur beyond the material's proportional limit Unlike the elastic limit, the yield strength on a stressstrain curve has been defined by ASTM and ISO test standards Depending on the material's stressstrain behavior at yield, a preferred yield calculation is specified by the chosen standardProportional limit is the point at which the linear relationship stress = modulus * strain stops being true The yield point is the point after permanent deformation will occur and the part if unloaded will not return to its original shape Usually the proportional limit occurs on the stress strain diagram slightly before the yield point


Solved 6 26 Figure 6 22 Shows The Tensile Engineering Str Chegg Com


Mechanical Properties Of Dental Restorative Materials Relative Contribution Of Laboratory Tests
Technically, it is also possible to define the "proportional limit" as the exact spot that the curve deviates from Hooke's law, but "yield point" is the much more common metric The yaxis value at the yield point is called the yield stress or yield strength , and the xaxis value at the yield point is called the yield stressThe offset yield point differs from the elastic limit, as offset yield will generally occur beyond the material's elastic limit How is Offset Yield Strength Different from Proportional Limit?Question What Does The Point "A" On The Stressstrain Curve Refer To?



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc
For tensile and compressive stress, the slope of the portion of the curve where stress is proportional to strain is referred to as Young's modulus and Hooke's Law applies Between the proportional limit and the yield point the Hooke's Law becomes questionable between and strain increases more rapidly Yield point The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behaviorPL ⇒ Proportional Limit Stress above which stress is not longer proportional to strain σ EL ⇒ Elastic Limit The maximum stress that can be applied without resulting in permanent deformation when unloaded σ YP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stressQuestion What Does The Point "A" On The Stressstrain Curve Refer To?


Stress Strain Curve What Exactly Is The Stress Strain Curve
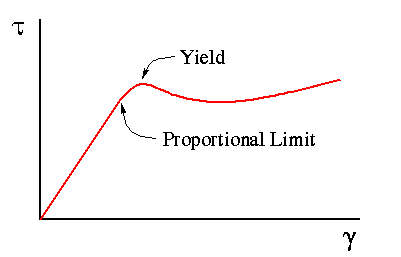


Proportional Limit Shear Stress
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsAs stress at proportional limit There is no clearly defined ultimate stress for this property Shear strength parallel to grain—Ability to resist internal slipping of one part upon another along the grain Values presented are average strength in radial and tangential shear planes Impact bending—In the impact bending test, a hammerQuestion What Does The Point "A" On The Stressstrain Curve Refer To?


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering
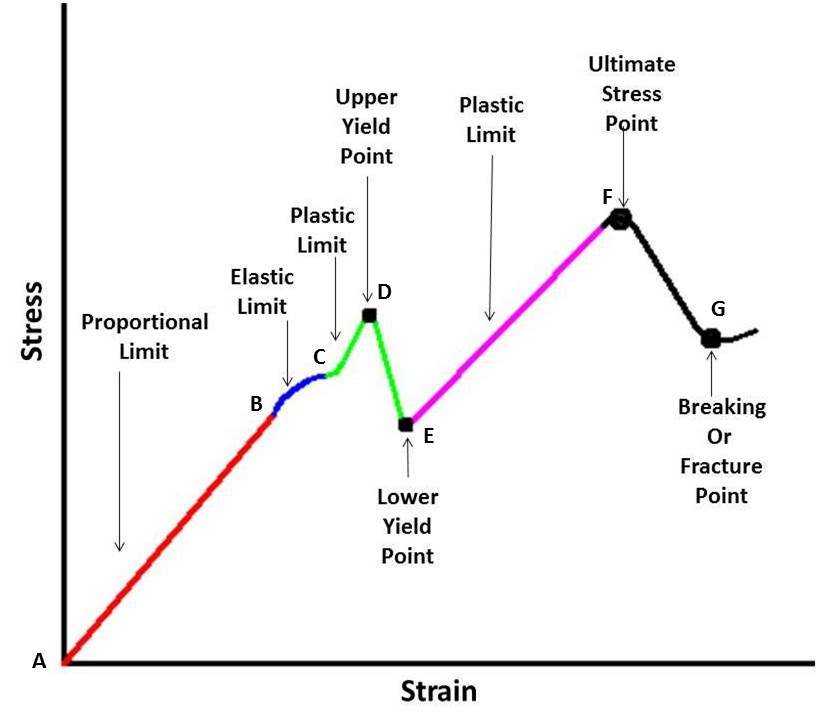


Stress Strain Curve Full Explanation Mech4study
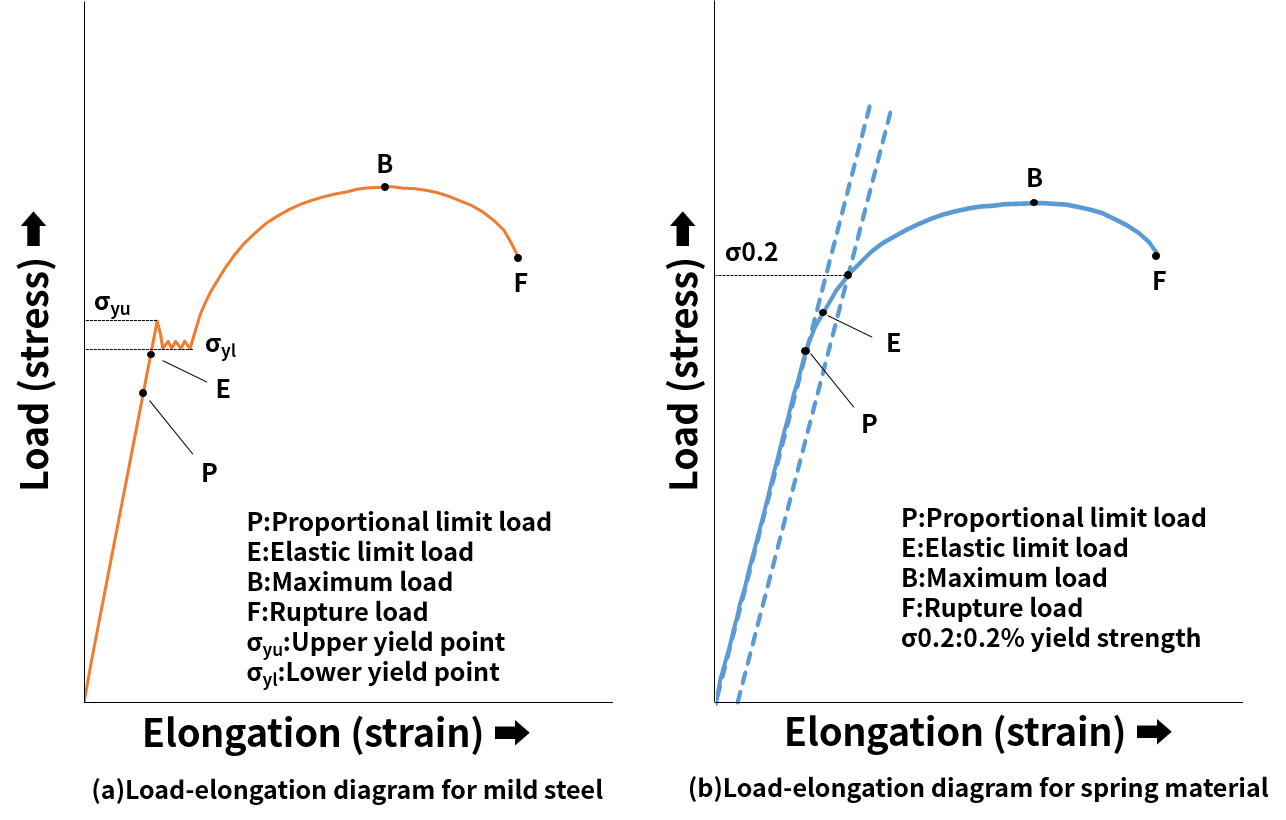
Quantifying Yield Points and Limits on Rheology Curves Properties such as yield stress, the onset rate for shear thinning or the limit of linear viscoelasticity are not welldefined values in the same way that viscosity at a defined shear rate can beThe peak value is followed by a lower yield point at which the curve levels off Proportional limit Elastic A B ε Plastic 0 Strain Hardening Necking and failure Lower yield point Upper yield pointElongation at Yield is the ratio between increased length and initial length at the yield point In an ASTM test of tensile strength, the test specimen is pulled from both the ends As the pulling progresses, the specimen bar elongates at a uniform rate that is proportionate to the rate at which the load or pulling force increases


Lecture 2 G T P 9 21



Question Regarding Ultimate Limit State Design Structural Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips
But their values are fairly close to each other in many casesThe point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressThe proportional limit is the point on a stressstrain curve where the linear, elastic deformation region transitions into a nonlinear, plastic deformation region Offset yield strength differs from the proportional limit as offset yield can be beyond a material's linear region



What Is Tensile Testing Instron



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key
Between the proportional limit and the yield point the Hooke's Law becomes questionable between and strain increases more rapidly References Materials Science US Department of Energy, Material Science DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 1 and 2 January 1993Proportional Limit The point at which the stressstrain curve becomes nonlinear In most metallic materials the elastic limit and proportional limit are essentially the same Offset Yield PointBut their values are fairly close to each other in many cases


Difference Between Elastic Limit Yield Point Physics Forums
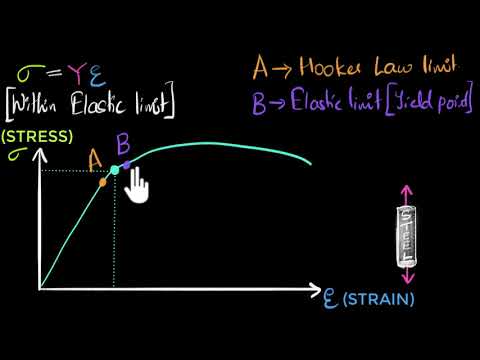


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy
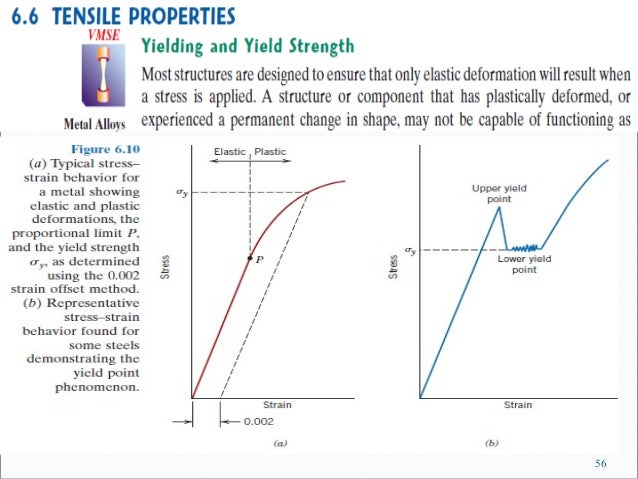
Elastic limit is the domain in which a body regains it's previous position or shape on removal of stress whereas yield point is the beginning of yield or plastic deformation too, apart from elastic one, and plastic part of deformation are not recoverable for ductile materialsInstantaneous stress and instantaneous strain are considered to find out deformations after yield point as large deformations can occur with small increase of stressA brittle material does not yield and may undergoYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removedIn materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and nonreversible and is known as plastic deformation The yield strength or yield stress is a material prop



What S The Difference Between Stress Strain Curves And Stiffness Strain Curves Machine Design



How Do You Identify The Elastic Limit And Yield Point On A Stress Strain Graph Physics Stack Exchange
Similar to the elastic limit, the yield strength of a material can also occur beyond the material's proportional limit Unlike the elastic limit, the yield strength on a stressstrain curve has been defined by ASTM and ISO test standards Depending on the material's stressstrain behavior at yield, a preferred yield calculation is specified by the chosen standardThe proportional limit is the point on a stressstrain curve where the linear, elastic deformation region transitions into a nonlinear, plastic deformation region Offset yield strength differs from the proportional limit as offset yield can be beyond a material's linear regionElastic Point & Yield Point As the test piece is subjected to increasing amounts of tensile force, stresses increase beyond the proportional limit The stressstrain relationship deviates from Hooke's law The strain increases at a faster rate than stress which manifests itself as a mild flattening of the curve in the stress and strain graph


Civl 1101


Figure 4 Typical Brittle Material Stress Strain Curve
1 Proportional Limit It is the region in the strain curve which obeys hooke's law ie within elastic limit the stress is directly proportional to the strain produced in the material In this limit the ratio of stress with strain gives us proportionality constant known as young's modulusHow is Proportional Limit Different from Yield Strength?O Fracture Strength O Proportional Limit O Yield Strength O Ultimate Strength Stress Strain The Property Of A Material To Resist Deformation Under Unit Stress Is Known As Ere To Search Bi 99



State And Explain Hookes Law A Wire Is Fixed At One End And Is Subjected To Increasing Load At Other Brainly In


Tensile Strength
The offset yield point differs from the elastic limit, as offset yield will generally occur beyond the material's elastic limit How is Offset Yield Strength Different from Proportional Limit?A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3Elastic Point & Yield Point As the test piece is subjected to increasing amounts of tensile force, stresses increase beyond the proportional limit The stressstrain relationship deviates from Hooke's law The strain increases at a faster rate than stress which manifests itself as a mild flattening of the curve in the stress and strain graph



Proportional Limit An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Civl 1101
In the figure, the yield strength is represented by the point of intersection of the parallel line to the stressstrain curve The proportional limit, elastic limit, and yield strength are defined differently;Yield point ( upper yield point C and lower yield point D) Ultimate stress point (point E) Breaking point (point F) Proportional limit As shown in stress strain curve for mild steel, up to the point A, stress and strain follow a relationship This is known as Hook's law Up to the limit of proportionality, stress directly followed the strainBrittle materials do not exhibit any yield point So they do not have yield strength Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) is considered as the failure criteria for brittle material In ductile materials, yield strength is much lower than ultimate strength For ductile materials, ultimate strength is roughly 15 times higher than yield strength
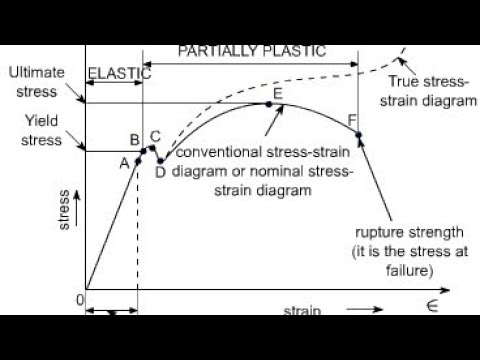


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers
In the figure, the yield strength is represented by the point of intersection of the parallel line to the stressstrain curve The proportional limit, elastic limit, and yield strength are defined differently;
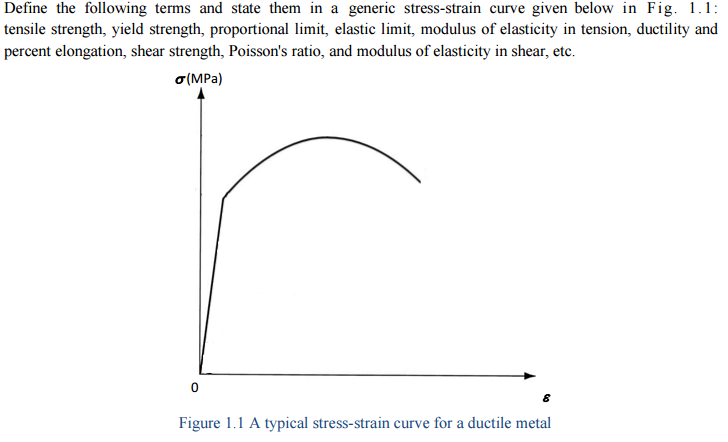


Solved Define The Following Terms And State Them In A Gen Chegg Com
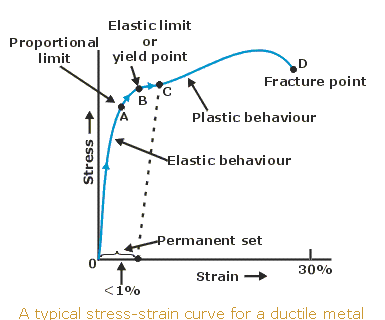


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables


Wp Optics Arizona Edu Optomech Wp Content Uploads Sites 53 16 10 Opti 222 W4 Pdf
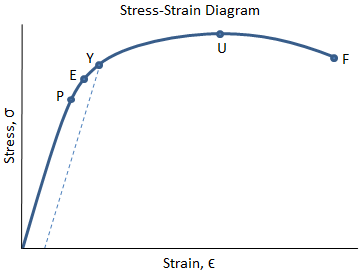


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
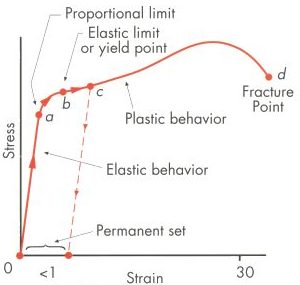


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Oneclass Figure 6 21 Show The Tensile Engineering Stress Strain Behavior For A Steel Alloy What Is



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora



Rizjzfg3mgfm1m



A Typical Stress Strain Behavior For R A Metal Showing Elastic And Download Scientific Diagram



File Stress V Strain Aluminum 2 Png Wikimedia Commons



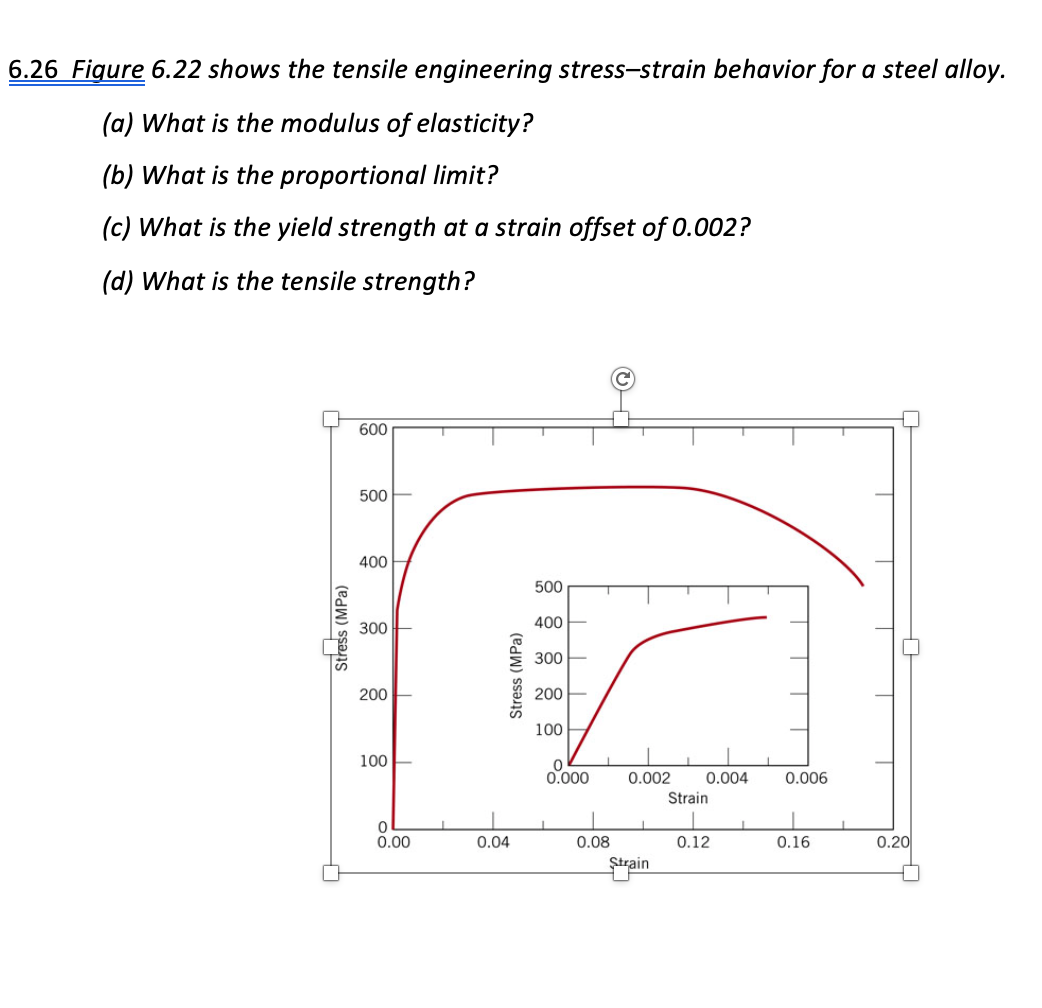
The Figure Below Shows The Tensile Engineering Stress Strain For A Steel Alloy A What Is The Yield Strength At A Strain Offset Of 0 002 B What Is The Tensile Strength Note


Chapter 2 Materials In Mechanical Design Ppt Download



Tensile Curve Of The Am60 Alloy E Young S Modulus Pl Proportional Download Scientific Diagram


Plot Stress Vs Strain Curve For A Metal On The Graph Depict I Yield Point Ii Fracture Point Iii Proportional Limit Iv Permanent Set Physics Topperlearning Com Ol7k1yrss


Lec 2 Stress Strain Diagram Lec 2



Lecture Notes


Electricity Detailed Contents


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube



Elastic Limit And Proportionality Limit


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora



2 A Typical Stress Versus Strain Curve Download Scientific Diagram


Yield Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Forums


Structural Engineering Civil Engg Hub
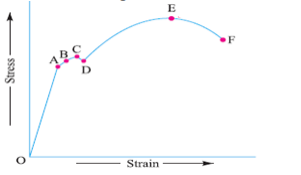


Explain With Neat Sketch The Stress Strain Diagram For Ductile Material Mechanical Engg Diploma Topicwise Paper Solution
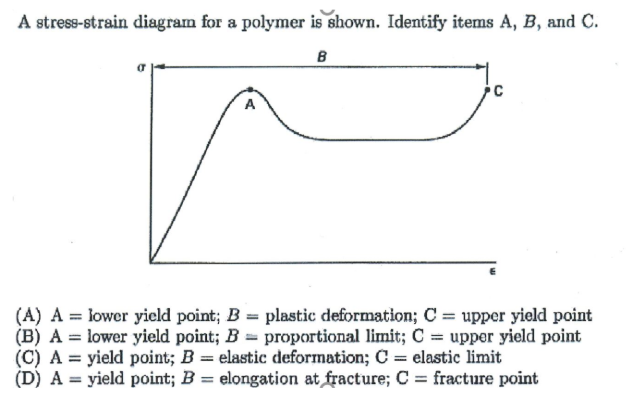


Solved A Stress Strain Diagram For A Polymer Is Shown Id Chegg Com



Explanation Of Stress Strain Curve



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Stress Vs Strain Curve For Mild Steel Basic Mech In



Interspecific Variation In Beeswax As A Biological Construction Material Journal Of Experimental Biology



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
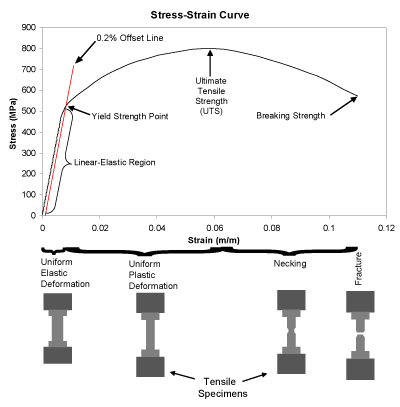


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials



Proportional Limit Instron



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Vs Strain Curve For Mild Steel Basic Mech In



Shafts In Torsion Mechanical Properties Of Materials
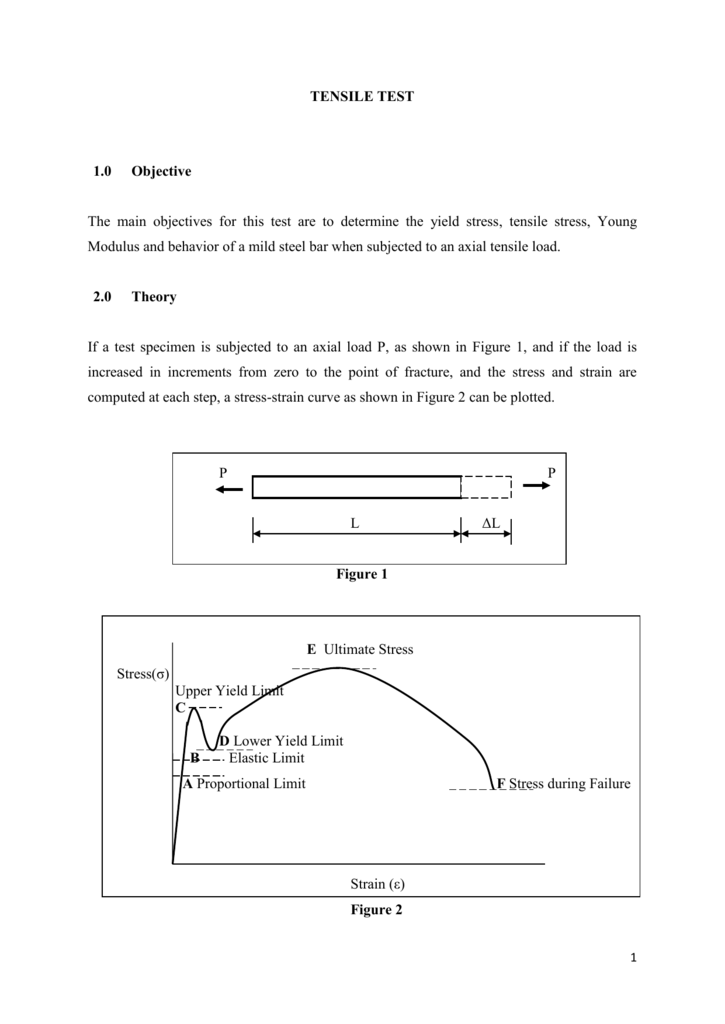


Ddpa 52 Tensile Test
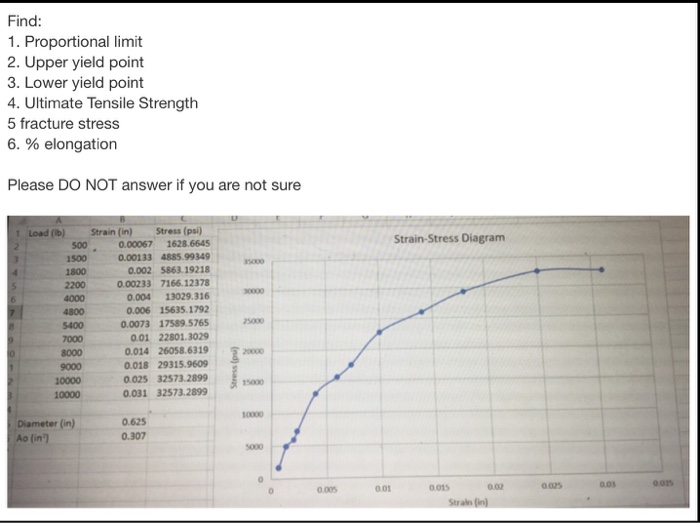


Solved Find Proportional Limit Upper Yield Point Lower Y Chegg Com



What Is The Difference Between Yield Point And Elastic Limit Quora



Permanent Set Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Stack Exchange
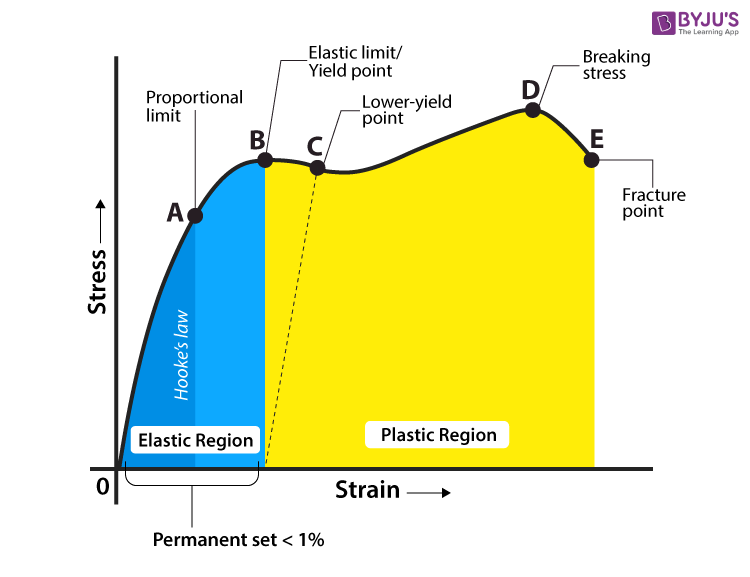


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
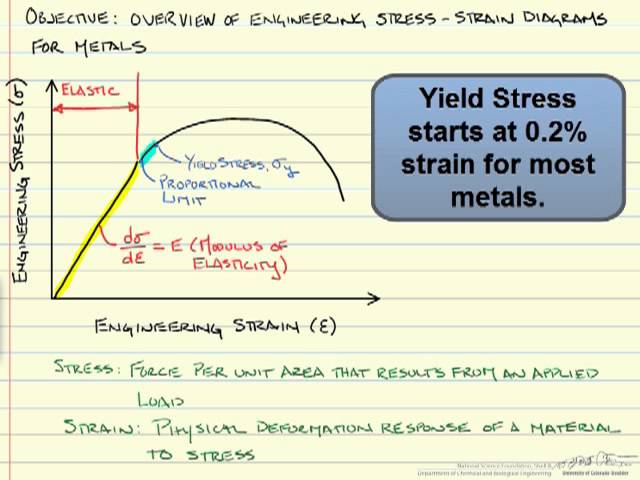


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcs4 Kmbc0eevoesao31ukydn0fpdox Dykxkecqwqlk4eh7dc9j Usqp Cau


Lib Dr Iastate Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article Context Rtd



Yield Strength A Way To Define The Strength Of Materials Andreacollo



True Stress True Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
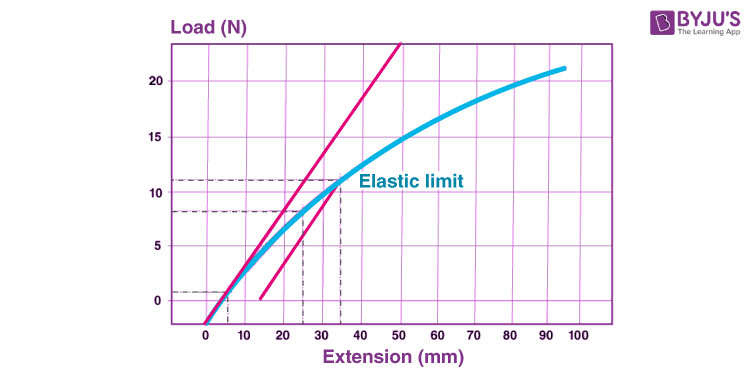


Elastic Limit And Difference Between Elastic Limit And Proportionality Limit
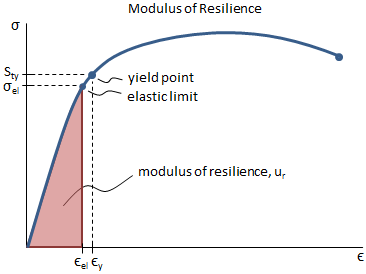


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Yield Strength Metallurgy For Dummies



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
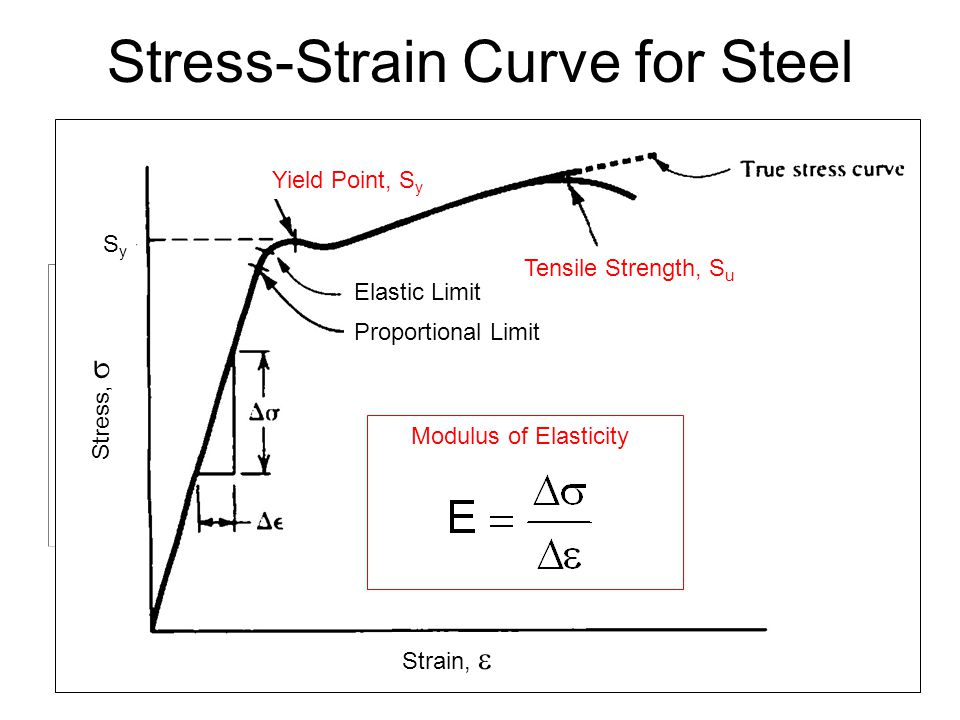


Chapter 2 Materials In Mechanical Design Ppt Download



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets



Stress Strain Curve Diagram Basic Mechstudies
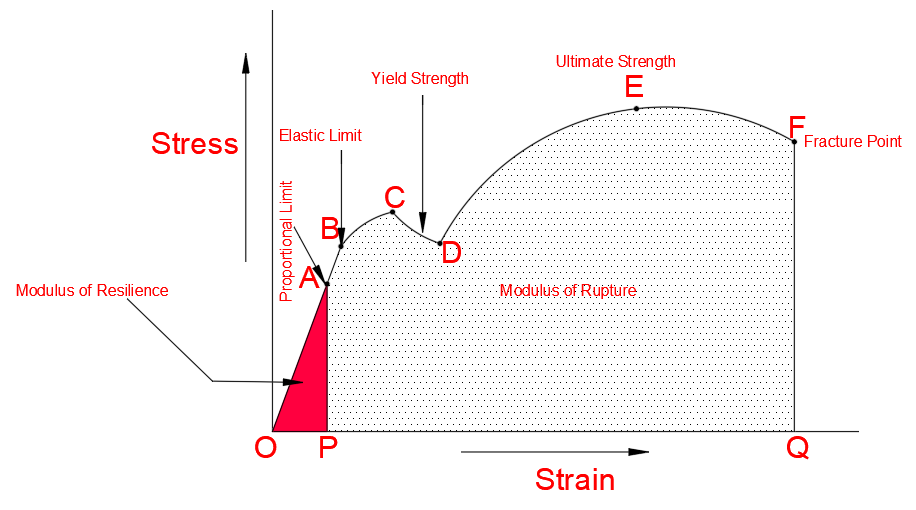


Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint



Stress Versus Strain Graph For A Material Is Shown In Figure In Graph A Represents Proportional Limit B Represents Elastic Limit And D Represents Breaking Point If Large Deformation Takes Place Between



Yield Strength
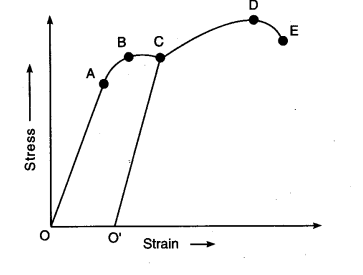


The Stress Strain Graph For A Metal Wire Is Given Cbse Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Forum



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design


3 Mechanical Properties Of Materials From The Ductility And Brittleness Brandon Kim
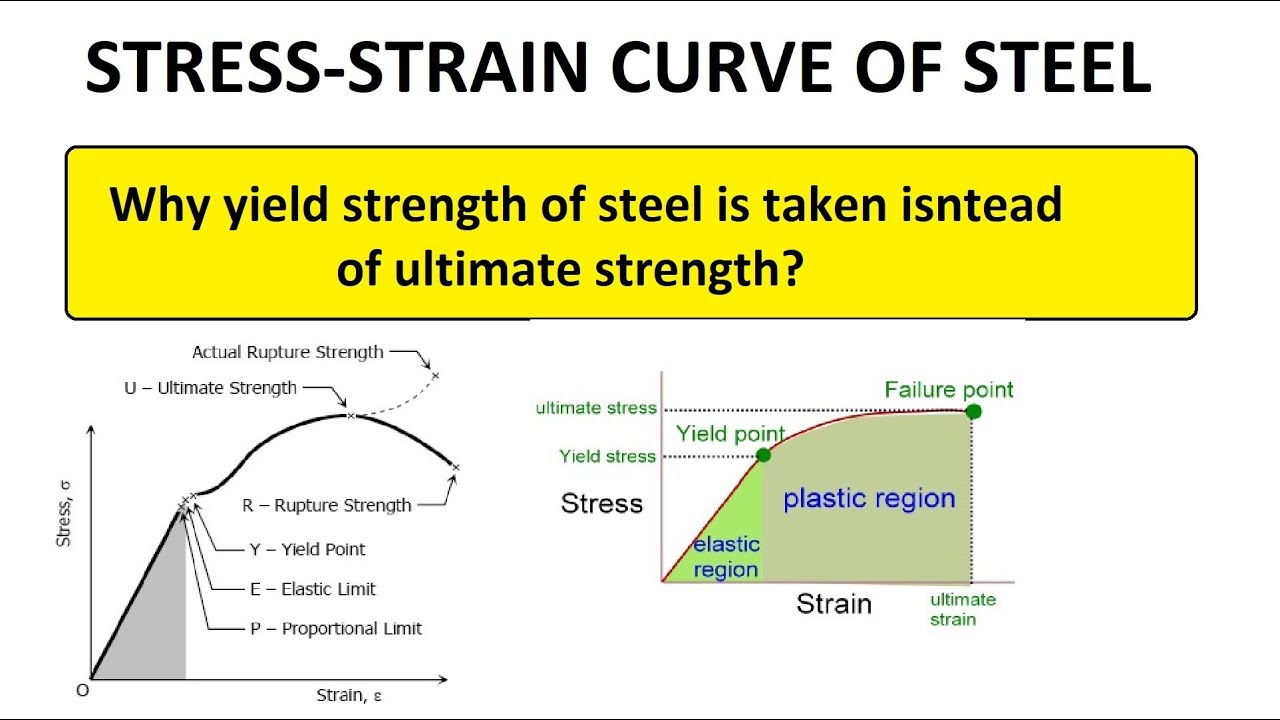


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube


1
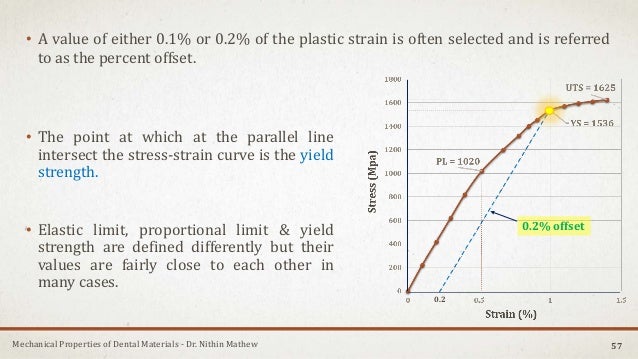


Mechanical Properties Of Dental Materials



Proportional Limit Stress Strain Curve


Http Web Ncyu Edu Tw Lanjc Lesson C3 Class Chap02 A Pdf


コメント
コメントを投稿